What Is the Difference Between a Series and Parallel Outlet?
When setting up electrical outlets, it’s important to understand the difference between series and parallel circuits, as each type has distinct characteristics and uses. In this article, we will explore the fundamental differences between series and parallel outlets to help you make the right choices for your electrical needs.
Circuit Configuration
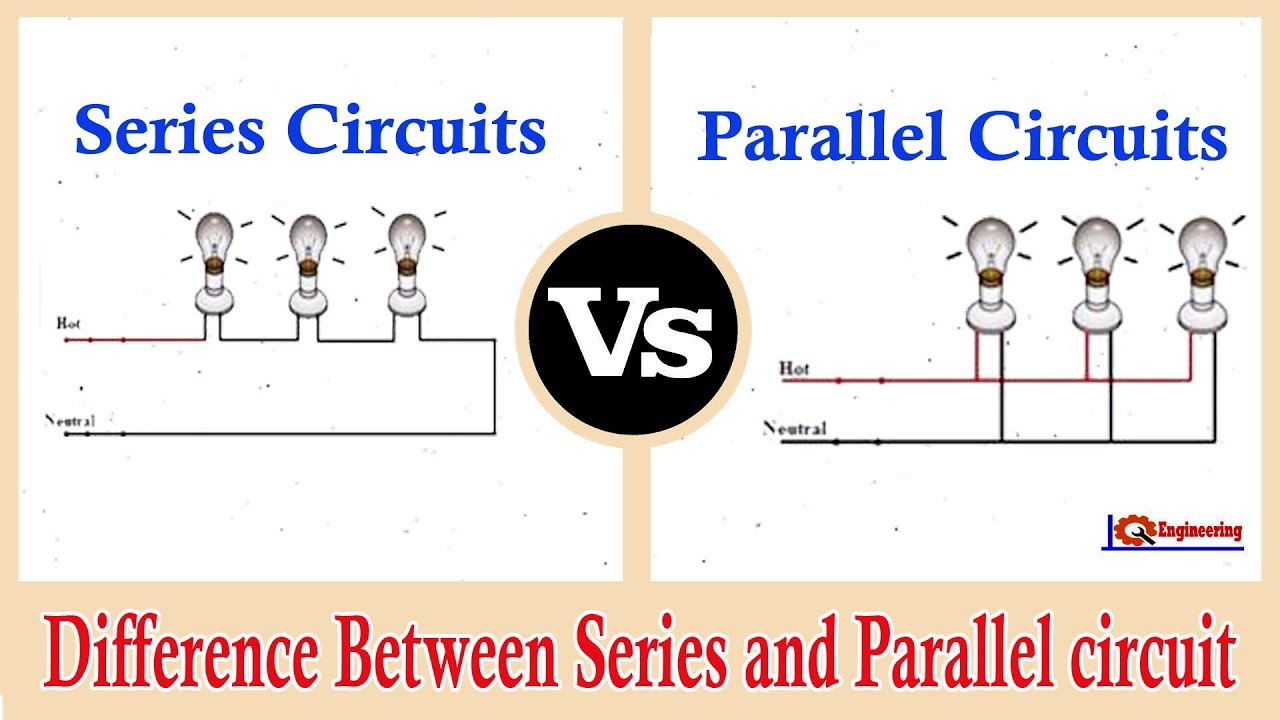
- Series Outlet: In a series circuit, electrical devices or outlets are connected one after the other in a single path. This means the current flows through each outlet in sequence, and if one device fails, the entire circuit is broken.
- Parallel Outlet: In a parallel circuit, the outlets are connected across multiple paths, allowing current to flow through each outlet independently. This means that even if one outlet fails, the rest will continue to function.
Voltage Distribution
- Series Outlet: The voltage is divided among the devices or outlets in a series circuit. Each device receives a portion of the total voltage based on its resistance.
- Parallel Outlet: In a parallel circuit, each outlet receives the full voltage from the power source. This ensures consistent performance across all devices.
Current Flow
- Series Outlet: The same current flows through all outlets in a series circuit. If the current exceeds the maximum rating for a device, it can cause overheating or damage.
- Parallel Outlet: The current is divided among the parallel outlets, with each device drawing its own current. This allows for more flexibility and reduces the risk of overloading.
Use Cases
- Series Outlet: Series circuits are rarely used for outlets in everyday applications because a failure in one device affects the whole circuit. However, they can be useful in specific scenarios, such as in certain types of sensors or in Christmas lights, where one bulb going out doesn’t necessarily break the entire string.
- Parallel Outlet: Parallel circuits are more common for household outlets and appliances. This setup ensures that each device operates independently, making it the preferred choice for wiring homes and businesses.
Safety Considerations
- Series Outlet: Since a failure in one part of the series circuit affects the entire system, series circuits can be less reliable and may present higher safety risks if one component malfunctions.
- Parallel Outlet: Parallel circuits are safer for everyday use. If one device fails, it does not interrupt the operation of the other devices on the same circuit, reducing the risk of complete power loss.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between series and parallel outlets is crucial when designing or troubleshooting electrical systems. Series circuits are suitable for specific applications, but parallel circuits are the most reliable and commonly used configuration for electrical outlets. By recognizing the advantages and limitations of each, you can make informed decisions when setting up or maintaining electrical installations.