Introduction to Series Circuits
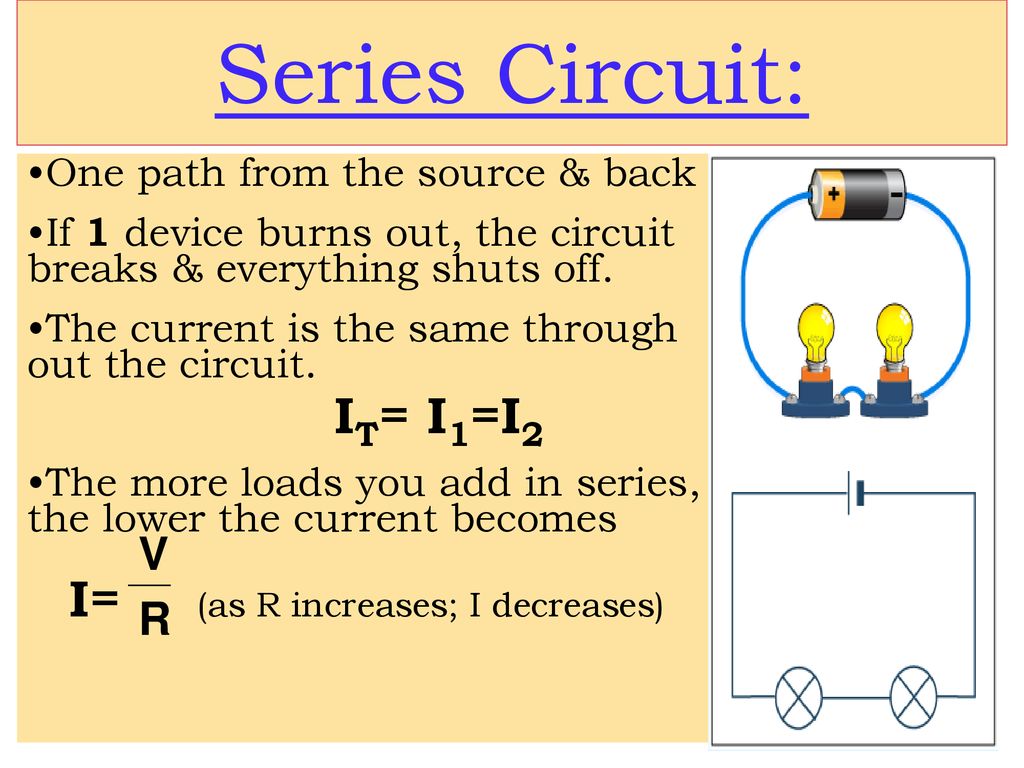
A series circuit is a type of electrical circuit in which components are connected end-to-end, forming a single path for the current to flow. The main characteristic of a series circuit is that the same current flows through all components. The total resistance in a series circuit is the sum of the individual resistances, and the voltage across the entire circuit is the sum of the voltages across each component.
Key Features of Series Circuits
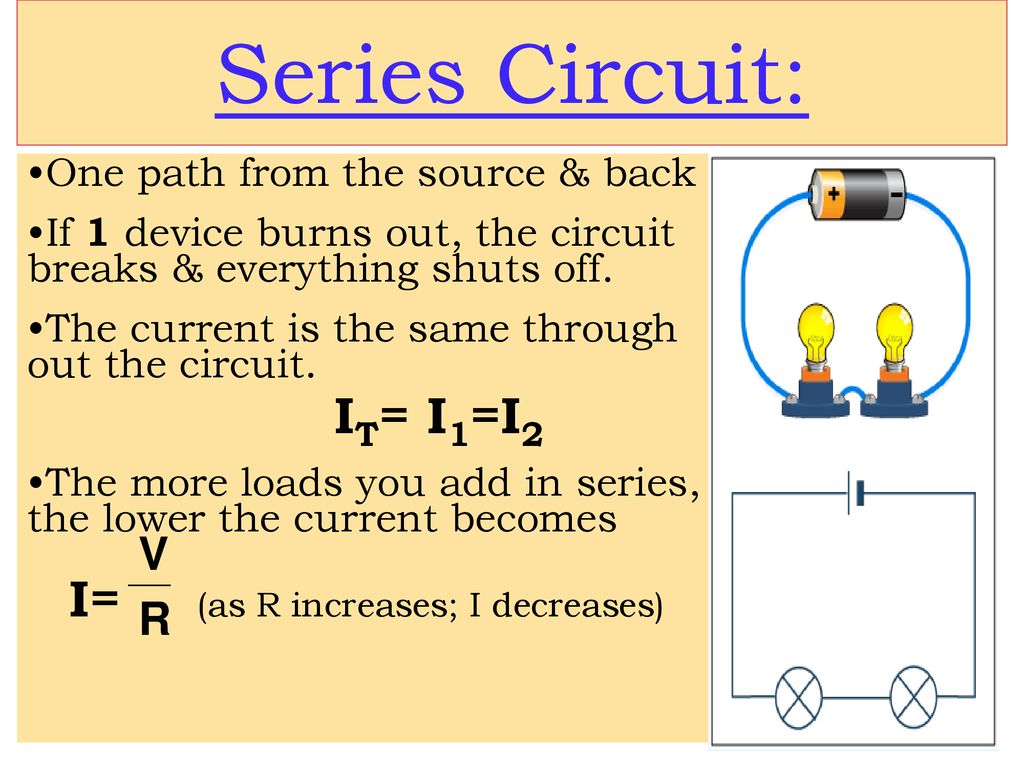
- Single Path for Current: In a series circuit, there is only one path for current to travel through, meaning if one component fails, the entire circuit is disrupted.
- Voltage Division: The total voltage is divided among the components based on their resistance. The sum of the individual voltages across each component equals the total voltage supplied by the source.
- Current is Constant: The current is the same through all components in the series. The only factor that varies is the voltage drop across each component.
Concept Development in Series Circuits (4-1)
Understanding series circuits requires familiarity with Ohm’s Law and basic circuit principles. In a series circuit, the total resistance (R_total) is the sum of individual resistances. This can be expressed as:
Rtotal=R1+R2+R3+…R_{\text{total}} = R_1 + R_2 + R_3 + \ldots
The current flowing through the circuit is determined by the total resistance and the source voltage using the formula:
I=VtotalRtotalI = \frac{V_{\text{total}}}{R_{\text{total}}}
Practical Applications of Series Circuits
Series circuits are commonly used in applications where the operation of multiple devices needs to be synchronized. A simple example is string lights, where all bulbs are wired in series. If one bulb fails, the entire string goes out, demonstrating the dependency of components in a series arrangement.
Advantages of Series Circuits
Simplicity: Series circuits are relatively simple to design and understand, making them ideal for basic applications.
- Easy to Control: Since the current is the same throughout the circuit, controlling the flow of electricity is straightforward.
Challenges of Series Circuits
- Dependency on Each Component: If one component fails, the entire circuit stops functioning.
- Voltage Distribution: The division of voltage among components can be problematic if the resistances vary significantly.
Conclusion
Series circuits are fundamental to understanding electrical principles. By mastering the concept development process and applying these principles, learners can build and troubleshoot series circuits effectively. Whether you are designing a simple circuit for a project or studying electrical engineering, grasping the essentials of series circuits is crucial for further advancements in electronics.