resistors in parallel equation When dealing with electrical circuits, one essential concept is the “resistors in parallel equation.” This equation is vital for calculating the total resistance while multiple resistors are linked in parallel.
Whether you are a scholar, hobbyist, or professional in electronics, knowledge of this equation lets you design and troubleshoot circuits greater effectively. In this complete guide, we can explore the resistors in parallel equations in detail, imparting clean reasons and sensible examples.
key takeaway
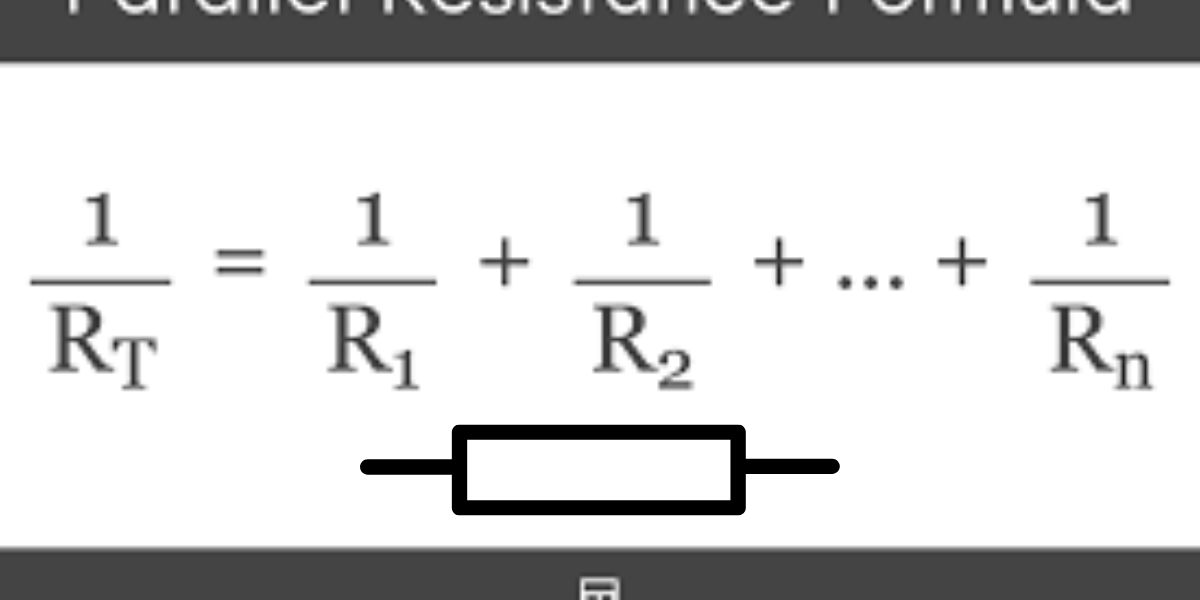
Mathematically, if R1,R2,R3,…,RnR_1, R_2, R_3, \ldots, R_n are resistors connected in parallel, the equivalent resistance ReqR_{\text{eq}} is given by:
1Req=1R1+1R2+1R3+⋯+1Rn\frac{1}{R_{\text{eq}}} = \frac{1}{R_1} + \frac{1}{R_2} + \frac{1}{R_3} + \cdots + \frac{1}{R_n}
To find ReqR_{\text{eq}}, calculate:
Req=1(1R1+1R2+1R3+⋯+1Rn)R_{\text{eq}} = \frac{1}{\left(\frac{1}{R_1} + \frac{1}{R_2} + \frac{1}{R_3} + \cdots + \frac{1}{R_n}\right)}
This formula indicates that:
- The total resistance in a parallel circuit is always less than the smallest resistance among the parallel resistors.
- Adding more resistors in parallel decreases the total resistance.
This is crucial for understanding how resistors affect each other in a circuit and for designing circuits with specific resistance values.
What are the Resistors in Parallel Equation?

What are the Resistors in Parallel Equation?
The resistors in parallel conditions are utilized to choose the identical resistance of resistors connected in a parallel setup. When resistors are related in parallel, the full resistance isn’t truly the sum of the person’s resistances. Instead, the reciprocal of the entire resistance is equal to the sum of the reciprocals of each character resistor’s resistance.
The Formula for Resistor in Parallel
To find the equivalent resistance ReqR_{eq} of resistors in parallel, you use the following formula:
1Req=1R1+1R2+1R3+⋯+1Rn\frac{1}{R_{eq}} = \frac{1}{R_1} + \frac{1}{R_2} + \frac{1}{R_3} + \cdots + \frac{1}{R_n}
Where:
- ReqR_{eq} is the equivalent resistance of the parallel resistors.
- R1, R2, R3,…, RnR_1, R_2, R_3, \ldots, R_n are the resistances of the individual resistors.
After calculating the sum of the reciprocals, you take the reciprocal of the result to find ReqR_{eq}.
Example Calculation
Suppose you have 3 resistors linked in parallel with resistances of four ohms, 6 ohms, and 12 ohms. To locate the equal resistance, you follow the resistors in the parallel equation as follows:
Calculate the reciprocal of each resistor’s resistance:
- 1R1=14=0.25\frac{1}{R_1} = \frac{1}{4} = 0.25 1R2=16≈0.167\frac{1}{R_2} = \frac{1}{6} \approx 0.167 1R3=112≈0.083\frac{1}{R_3} = \frac{1}{12} \approx 0.083
- Add these values together:1Req=0.25+0.167+0.083=0.5\frac{1}{R_{eq}} = 0.25 + 0.167 + 0.083 = 0.5
- Take the reciprocal of the result:Req=10.5=2 ohmsR_{eq} = \frac{1}{0.5} = 2 \text{ ohms}
Thus, the equivalent resistance of the three resistors in parallel is 2 ohms.