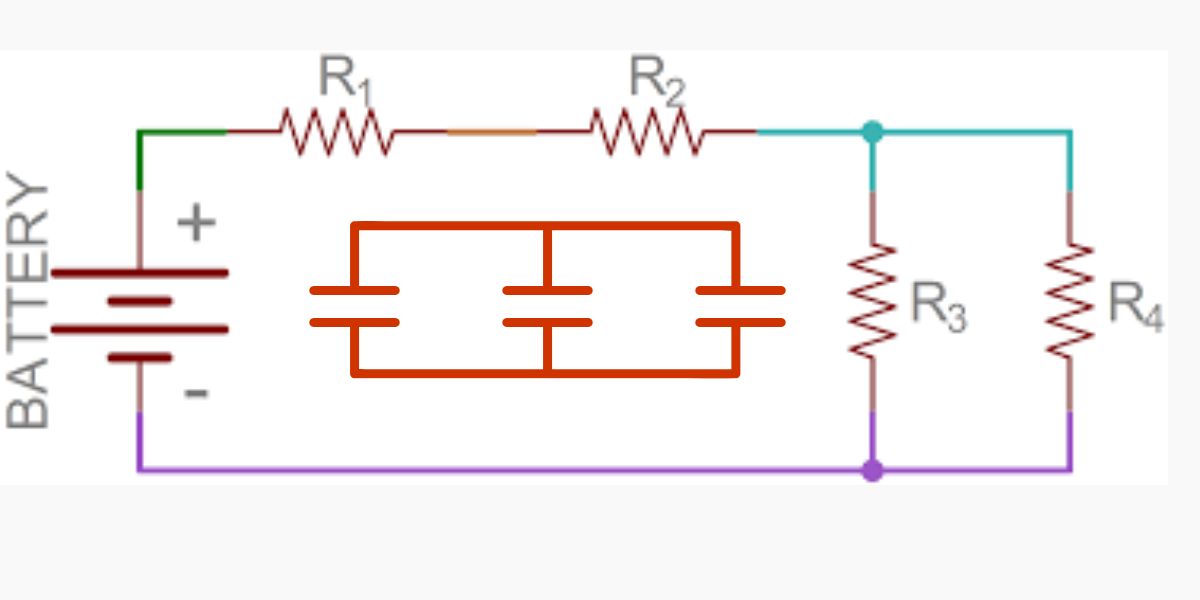
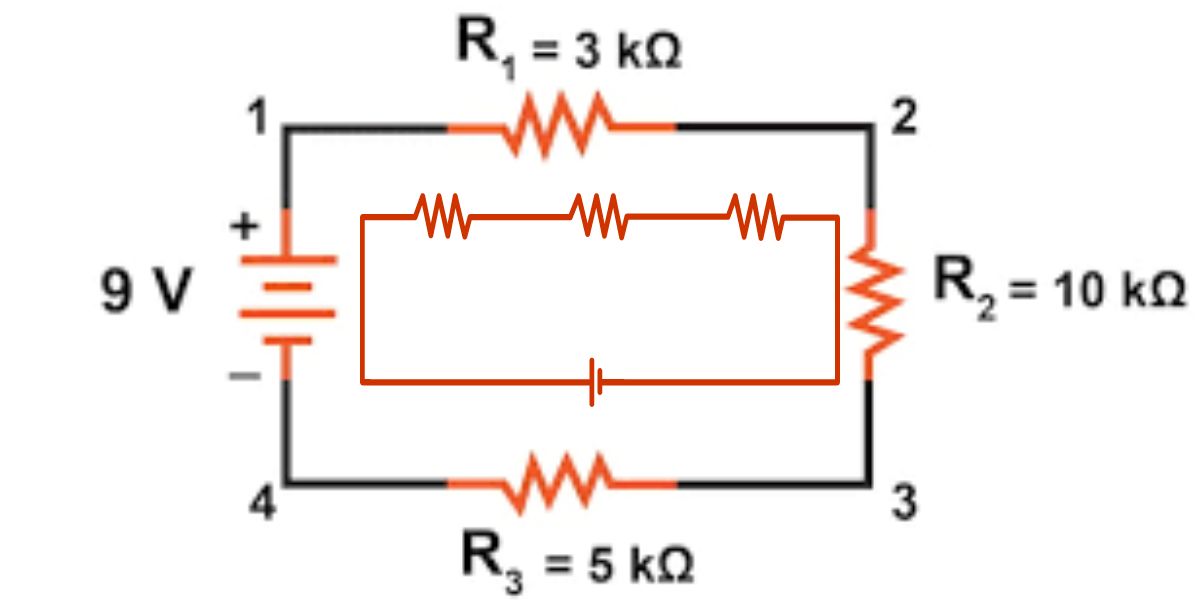
What are examples of series-parallel circuits? COMBINING RESISTORS IN Arrangement AND PARALLEL CIRCUITS IS Fundamental Information TO Anybody Craving TO TINKER WITH Hardware. These circuits are fundamental in most electrical frameworks, from family apparatuses to mechanical hardware.
This article aims to look at different **Kinds of series-parallel circuits, their features and uses**, to help the reader understand their application. Regardless of whether you are a learner, a do-it-yourselfer, or inquisitive, this guide will give you a vivid knowledge of series-parallel circuits.
What Are Series and Parallel Circuits?
Before we go further ahead with **examples of series-parallel circuits** it is important to distinguish between series and parallel circuits.
Series Circuits
A series circuit is one in which components are joined end to end so that the current flows through one component and then along the next in turn. This implies that the same current circulating through the various branches is the same while voltage shares the various sections within the circuit. If any one component in the circuit becomes out of order the flow of current is stopped.
Parallel Circuits
The circuit whose components are joined in parallel are in series across different points or junctions such that several paths for current are available. All the components get the same voltage; however, the current is split between the various available paths. The last is that a failure in one path does not disturb the other components, which allows for recovering from an error.
What Are Examples of Series-Parallel Circuits?
Series(parallel) circuits are those in which some components are arranged in series while others are arranged in parallel. In this way, they can provide advantages of both kinds of circuits, which seem to be profitable for the company. Here are some common examples: Here are some common examples:
Household Wiring Systems
For the lighting and power outlet regulation in household electrical systems **series parallel circuits** are employed. For example, a series-parallel circuit can be used to define circuitry for lighting-specific outlets or light fixtures so that each may be controlled independently.
Example
Think of a circuit with many bulbs connected in parallel but each parallel group of bulbs is connected in series with a switch. Through this arrangement, it is possible to note that if the bulb in a particular circuit blows, the other bulbs for the same circuit continue to be lit. However, the switch regulates the circuit at large or the entire circuit if one is to assume the smaller loops are circuits in their own right.
Automotive Electrical Systems

Automotive Electrical Systems
The commonly used circuits in automotive electrical systems include **series parallel circuits** commonly used to power electrical appliances such as headlights, rear lights, and interior lights among others.
Example
Suppose you have an automobile that includes two headlight facilities. The headlights might also be wired in parallel so that each bulb gets the same voltage as the other so that a bulb can work on its own. However, the parallel groups of headlights might be connected in series with a fuse regarding the protection the circuit against overload.
Battery Packs
In battery packs, the circuits applied are **series parallel circuits** by which the voltage and the capability can be controlled. Batteries can be connected in series and/or parallel arrays to elevate the total performance of the pack.
Example
One of the common configurations that are used is where several batteries are connected in series to achieve higher voltage only to have these series-connected batteries connected in parallel to achieve a higher capacity of the battery pack. For instance, one battery pack could be made up of 12 batteries connected in series to give 12V and several such strings in parallel adding up to 10,000 mAh.
Power Supply Units (PSUs)
Computer and industrial equipment’s power supply unit employs **series parallel circuits** for power supply distribution.
Example
On the nature of AC-DC conversion On a computer power supply unit, several parts may require varying voltages. The PSU might employ a series of parallel circuits to regulate the main voltage into multiple necessary voltages, including, 5V, 12V, as well as 3V. 3V. The internal circuits have the responsibility of making sure that each of the voltages is supplied to the proper components.
Home Appliances
Home appliances also rely on a series of parallel circuits to work and offer security to the users. For example, the microwave oven may incorporate both series and parallel circuits for the turntable, light, and magnetron respectively.
Example
In a microwave oven, it could also be seen that the turntable motor is in parallel with the light bulb. Each of these components could be adjusted using a single switch but this switch would have to be connected in series with the circuit. This enables independent operation of the turntable and the light but they are managed using a single switch.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Series-Parallel Circuits
Advantages and Disadvantages of Series-Parallel Circuits
To opt for the kind of **series parallel circuits** that will be beneficial in a certain situation, one must familiarize oneself with the perks and cons associated with the setup.
Advantages
- Flexibility: Lesser disadvantages include the fact that the circuit can easily be adjusted by removal or addition of components without having to affect the whole system in series-parallel circuits.
- Redundancy: These circuits function in parallel, and often they include redundancy; this is, if a component fails other components may still function.
- Controlled Voltage and Current: They enable the appropriate setting of voltage and current to the diverse components, and are thus appropriate for sophisticated systems.
Disadvantages
- Complexity: Unlike the cascaded series circuit or pure parallel circuit, it is generally somewhat more difficult to design and solve for the series-parallel circuits.
- Power Losses: In this connection, series-parallel circuits have some demerits for example; they undergo power loss if inappropriately designed due to poor connections and resistance.
- Cost: By using series-parallel circuits, they may call for more components and the procedures are slightly elaborate and hence costly.
How to Design Series Parallel Circuits
Designing a series-parallel circuit involves several steps:
- Determine Requirements: Determine the voltage and current of each element.
- Choose Configuration: Depending on how you would wish to distribute the voltage and current, the decision on the positioning of the series or parallel can be made.
- Calculate Values: Apply the concept of Ohm’s Law and Kirchhoff’s Laws in the determination of resistance, current, or voltage in the circuit.
- Draw Circuit Diagram: You can draw a map to outline how the circuits should be laid out.
- Assemble Components: Solder the components as shown in the diagram and attempt to make the circuit function as expected.
FAQs
What Is the Difference Between Series and Parallel Circuits?
In a series circuit, the components are arranged in a chain-like manner and the current is the same in all the components. The basic difference between series and parallel circuits is that in the former, components are joined at specific points while in the latter, they are connected across the terminals in such a way that each of these components gets the same voltage.
How Do Series Parallel Circuits Work?
Series parallel circuits come as an integration of the series and parallel circuits. Some components can be connected in series with other components in one part of the circuit and parallel to another part of the circuit to achieve the advantages of both situations.
What Are Some Common Applications of Series-Parallel Circuits?
Some of the typical uses of these are in residential circuits, car electrical systems, batteries and packs, power supplies, and home appliances.
Why Are Series Parallel Circuits Used?
They are applied to acquire the favorable characteristics of both series and parallel connections, including flexibility, redundancy, and voltage as well as current settings to fulfill the special needs of intricate electrical networks.
Can Series Parallel Circuits Be Used for High-Power Applications?
Yes, series-parallel circuits can be made to supply high power if adequate calculations are made involving the components to prevent the circuit from getting hot and in the addition of protecting mechanisms within the circuits.
Conclusion
Series parallel circuits are widely used in present-day electronics and electrical systems. Hopefully, knowing about examples of series-parallel circuits and how they can be used, will help you to comprehend their function concerning the electrical flow, flexibility, and dependability. Due to their efficiency, these circuits are used to distribute electrical energy in-home wiring and industrial power supplies.
And if one is in the process of either designing a new circuit or trying to analyze and solve a faulty circuit then it is mandatory to have a basic understanding of series parallel circuits.
Please, you may always come back to this article to revise the content on the series of parallel circuits and their uses.