In the domain of electrical circuits, Series circuits play a vital part in understanding how power streams through different components.
One common arrangement is an arrangement circuit containing two gadgets. This article digs into the complexities of such circuits, shedding light on their structure, working, and down-to-earth applications.
Key Takeaways:
- Definition of Series Circuit: A series circuit is a configuration where components are connected in a sequence, forming a single path for the flow of electric current.
- Components: In a series circuit with two devices, two electrical devices (e.g., resistors, bulbs, etc.) are connected end-to-end, allowing the current to pass through each sequentially.
- Voltage Distribution: The voltage across each device in a series circuit adds up to the total voltage of the circuit.
- Current Flow: The current remains constant throughout a series circuit, flowing through each device in the circuit.
- Resistance: Total resistance in a series circuit is the sum of individual resistances.
What is a Series Circuit?
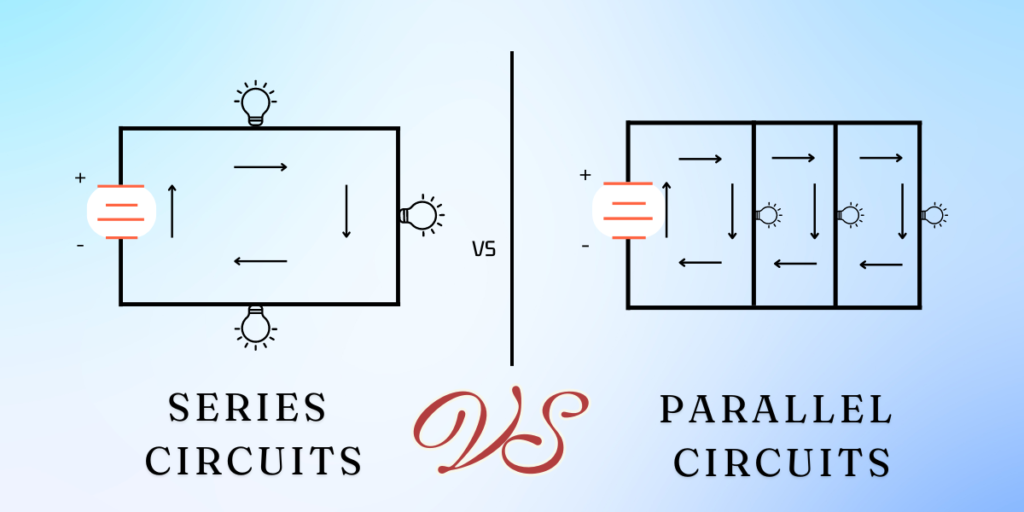
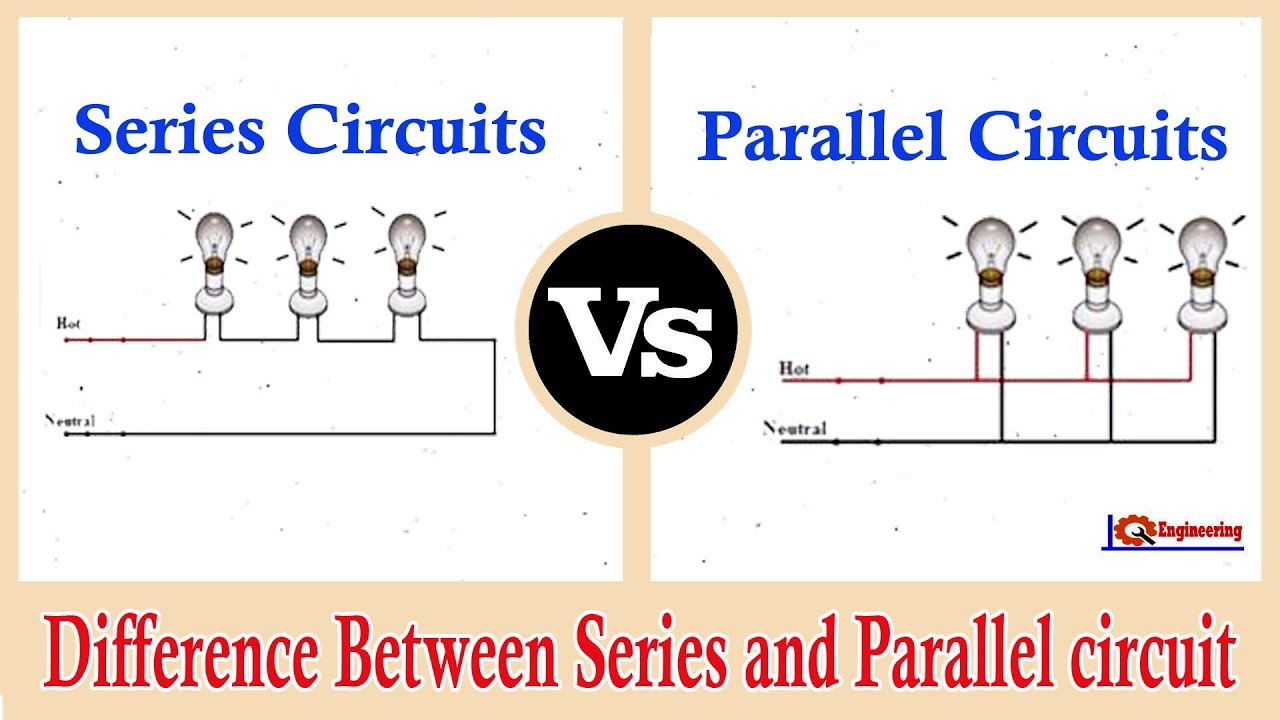
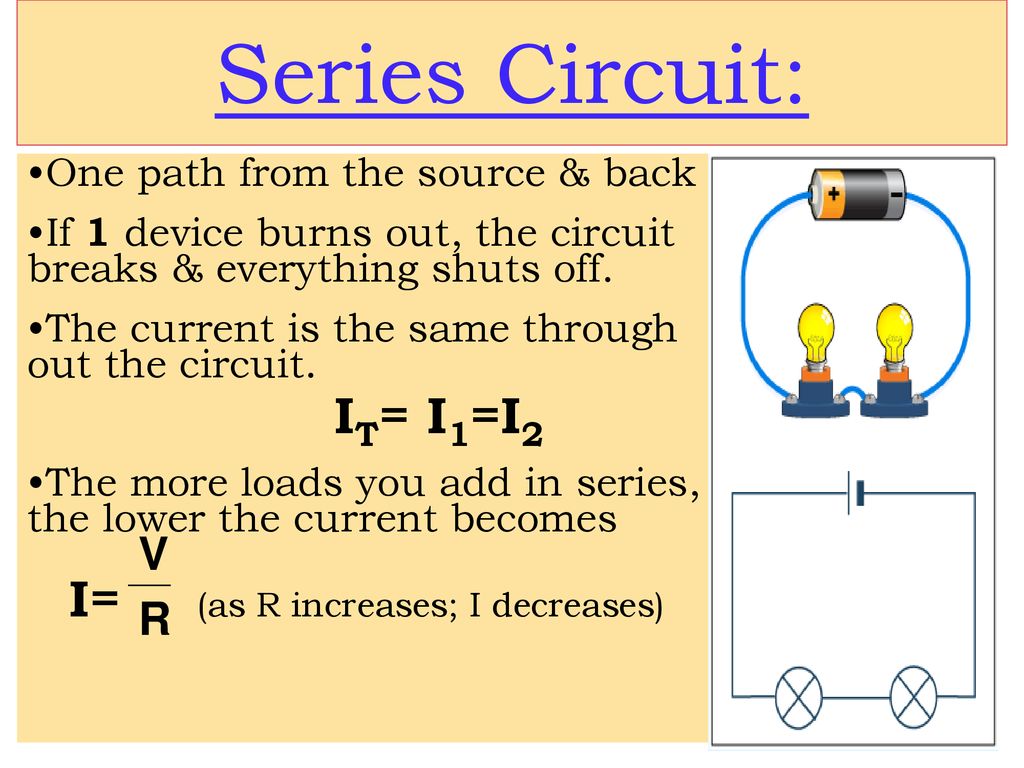
An arrangement circuit is a closed circle where the components are associated conclusion to a conclusion, shaping a single way for the current to stream.
In this arrangement, the same current passes through each component in the circuit. When two gadgets are associated in arrangement, they share the same current, making it a fundamental concept in electrical building and electronics.
Components in a Series Circuit
In an arrangement circuit containing two gadgets, the gadgets seem to be any electrical components such as resistors, bulbs, or indeed more complex gadgets like engines. These gadgets are associated consecutively, with one gadget specifically taking after the other.
Understanding Gadget Interaction
In an arrangement circuit, the behavior of one gadget straightforwardly impacts the other. When two gadgets are associated in arrangement, their resistances include up to make an add-up to resistance in the circuit.
This adds up to resistance deciding the stream of current through the circuit agreeing to Ohm’s Law, which states that current is contrarily corresponding to resistance.
The Part of Voltage in Series Circuits

A Series Circuit Contains Two Devices
In an arrangement circuit, the voltage over each gadget depends on its resistance and adds up to current streaming through the circuit.
Concurring to Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law, the entire amount of voltages over all gadgets in an arrangement circuit rises to the add up to voltage connected to the circuit.
Practical Applications
Series circuits with two gadgets discover applications in different areas, counting family wiring, car gadgets, and mechanical apparatus.
For occurrence, in a basic spotlight, the batteries and the bulb are frequently associated in arrangement to give reliable illumination.
Advantages and Disadvantages
One advantage of arrangement circuits is their straightforwardness, making them simple to get and actualize. In any case, one drawback is that if one gadget in the arrangement comes up short or is expelled, the whole circuit will be hindered, driving to a misfortune of function.
Advantages of Series Circuits
- Simplicity: Arrangement circuits are clear, making them awesome for learning about electricity.
- Ease of Understanding: Since the current streams through each gadget in turn, it’s simple to anticipate how the circuit will behave.
Disadvantages of Series Circuits
- Single Point of Disappointment: If one gadget stops working, it hinders the entire circuit.
- Increased Resistance: Including more gadget increments that add up to resistance, which can diminish the proficiency of the circuit.
Table: Comparison of Series Circuits with Two Devices
| Aspect | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|
| Simplicity | Easy to understand and implement. | If one device fails, the entire circuit stops working. |
| Predictability | Predictable behavior as current flows sequentially through each device. | Adding more devices increases total resistance, reducing efficiency. |
FAQs about A Series Circuit Contains Two Devices
Q: What happens if one gadget in an arrangement circuit fails?
If one gadget in an arrangement circuit comes up short, it hinders the stream of current through the whole circuit, causing all gadgets to halt functioning.
Q: How can I calculate the add-up to resistance in an arrangement circuit with two devices?
To calculate the add-up to resistance in an arrangement circuit, essentially include the personal resistances of the two gadgets together.
Q: Can I include more than two gadgets in an arrangement circuit?
Yes, you can include numerous gadgets in an arrangement circuit. Each extra gadget increments the add up to the resistance of the circuit.
Conclusion
Understanding the arrangement circuit of two gadgets is crucial in the ponder of gadgets and electrical designing.
Thecirculationsits offer important experiences in the interaction between components and the stream of current.
By getting a handle on the concepts sketched out in this article, perusers can pick up a more profound understanding of arrangement circuits and their viable applications in different areas.